You Can Respond to Phishing Threats in Seconds with Cofense and Cyware: Here’s How
All organizations will be phished, but they don’t have to experience a reputation-damaging breach. The best defense is a combination of aware employees, purpose-built phishing solutions, automated incident analysis and response playbooks, and a repeatable process that scales as fast as attackers innovate.
Targeted and relentless. Threat actors pinpoint organizations to steal credentials, infect endpoints, encrypt data for ransom, or exfiltrate intellectual property or non-public information.
The security workflow is preceded by conditioning employees to recognize suspicious email and report to their security team. What happens next is a blend of technology and intelligent analysts who have the right information to make an informed decision without negatively impacting the business.
Cofense and Cyware have partnered to provide organizations with the resources to collect phish that evade secure email gateways (SEGs), automate the analysis, and determine threat severity in seconds.
- Phish evade the SEG
- Employees report the suspicious email
- Cofense TriageTM ingests and analyzes one or more email clusters with similar tactics
- Cyware CSOL (security orchestration platform) ingests indicators from Cofense Triage
- Cyware CTIX (threat intelligence platform) enriches indicators from Cofense Triage with Cofense IntelligenceTM and other premium intelligence sources
- Cyware CSOL runs a complete response playbook which may include blocking a URL at the network gateway to protect employees from reaching the external phishing site
Let’s look at the sequence of events and how the response is carried out.
The use case is simple, and the process is effective:
2. A conditioned employee reports the email that evaded the SEG to a predetermined abuse mailbox monitored by the SOC. Purpose-built Cofense Triage ingests all emails from the abuse mailbox and automatically analyzes to quickly remove benign reports while at the same time highlight real threats.
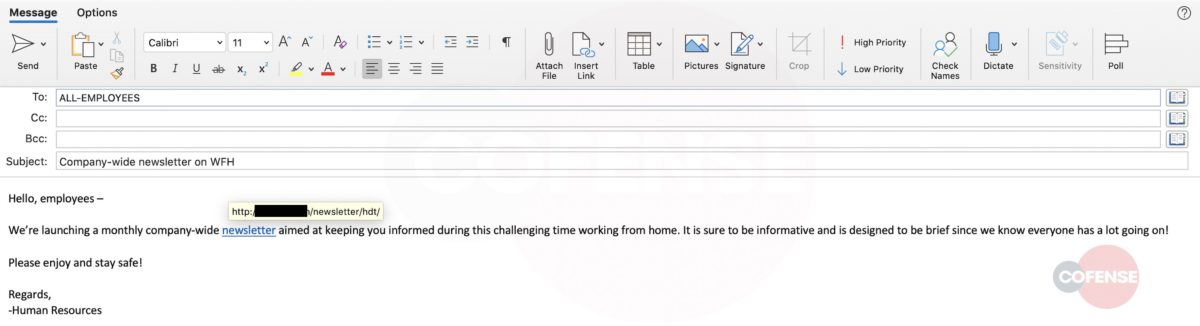
- Phisher crafts their email (figure 1) and in this case is attempting to direct the employee to a malicious site where a payload could infect the endpoint.
Figure 1. Malicious link within a company-wide email portraying to be from HR
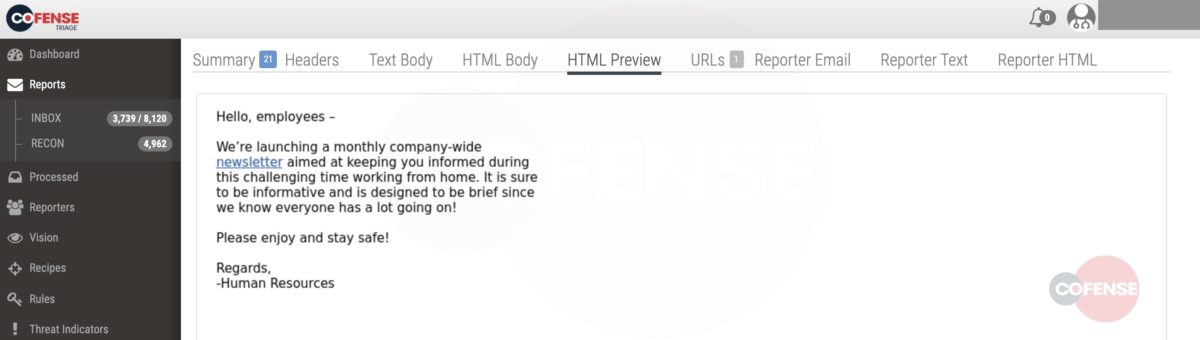
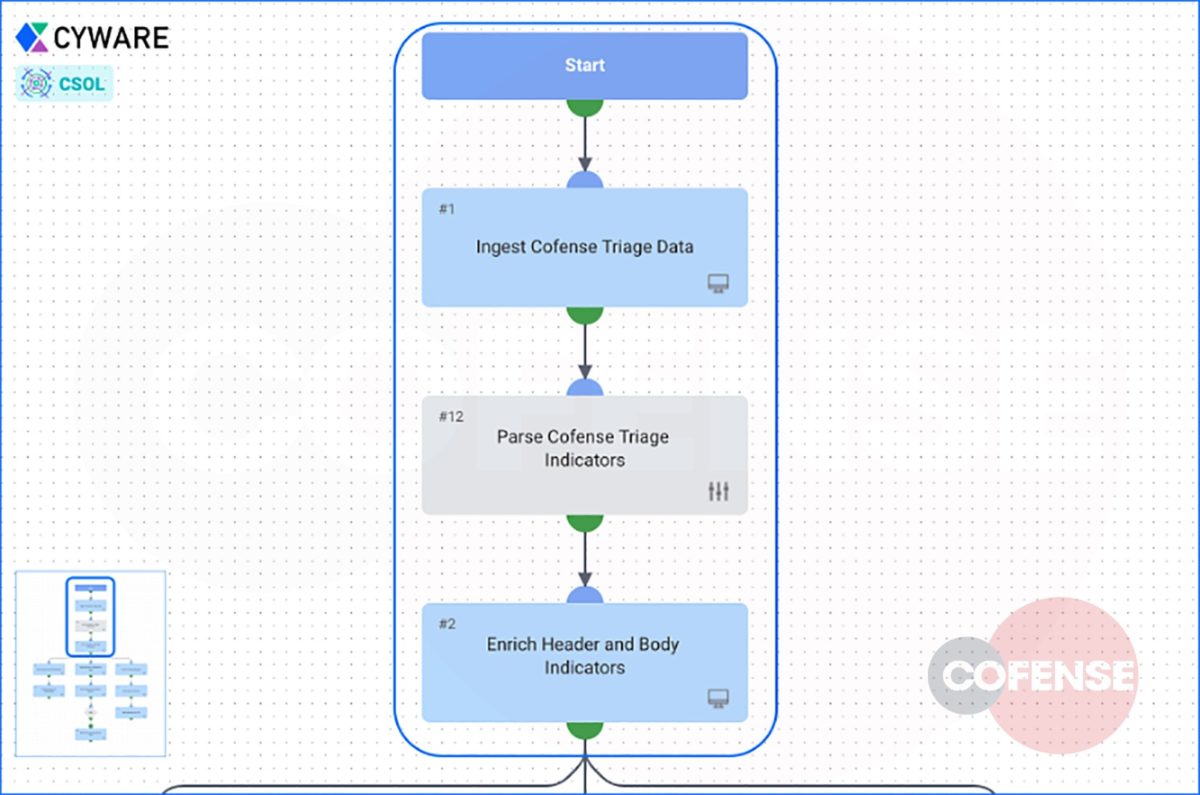
3. Upon ingestion into Cofense Triage, out-of-box phishing rules are applied, and automated analysis categorizes the email as ‘advanced threats’, matching Emotet indicators and tactics. Benign emails are not impairing the view and the SOC can focus on credible phishing threats from a highly reputable reporter (in this case, a VP within the company).
Figure 2. Reported email ingested into Cofense Triage for automated analysis
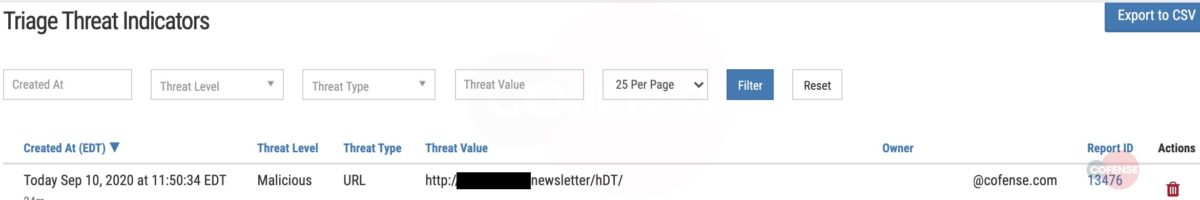
4. Knowing this email is dangerous, the URL is designated malicious by an analyst
Figure 3. Processed email matching advanced threats Emotet rules
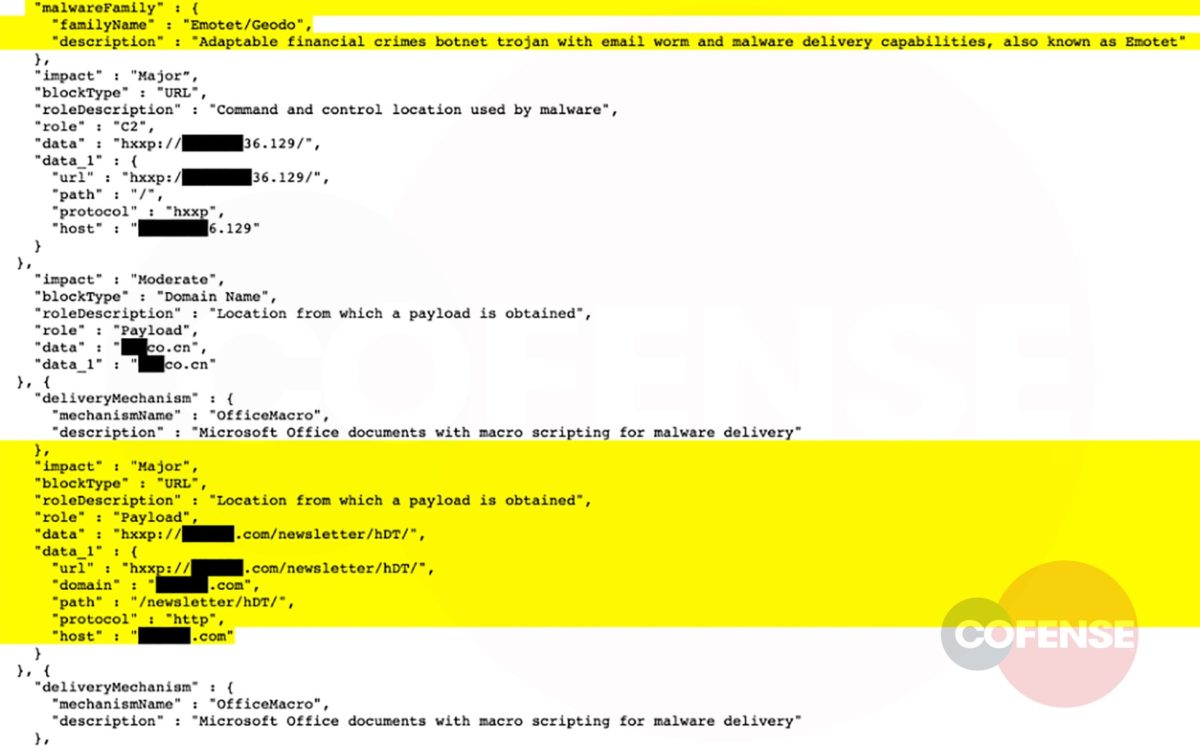
5. Additional validation within Cofense Intelligence further confirms the URL is malicious and delivers analysts related phishing indicators that, in this example, are part of the Emotet malware family. Other domains, files, and URLs are returned from knowing just one threat indicator.
Figure 4. SOC analyst verifying malicious threat indicator
6. Once Cofense has confirmed that the URL is malicious, the analyst can leverage the orchestration capabilities of the Cyware Security Orchestration Layer (CSOL) to take action and begin remediation and triage efforts. CSOL gives users the ability to create automated, customizable workflows that easily integrate with the other tools in their security stack.
Figure 5. Cofense Intelligence JSON output snippet with additional threat indicators
Figure 6. CSOL ingests Cofense Triage phishing data
In this example, the analyst initiated the Cofense Triage Playbook to ingest the data it received from the Cofense Triage API. The playbook parsed the available data from Cofense to find the associated indicators, and then leveraged integrations with their other enrichment tools to fully enrich all associated indicators.
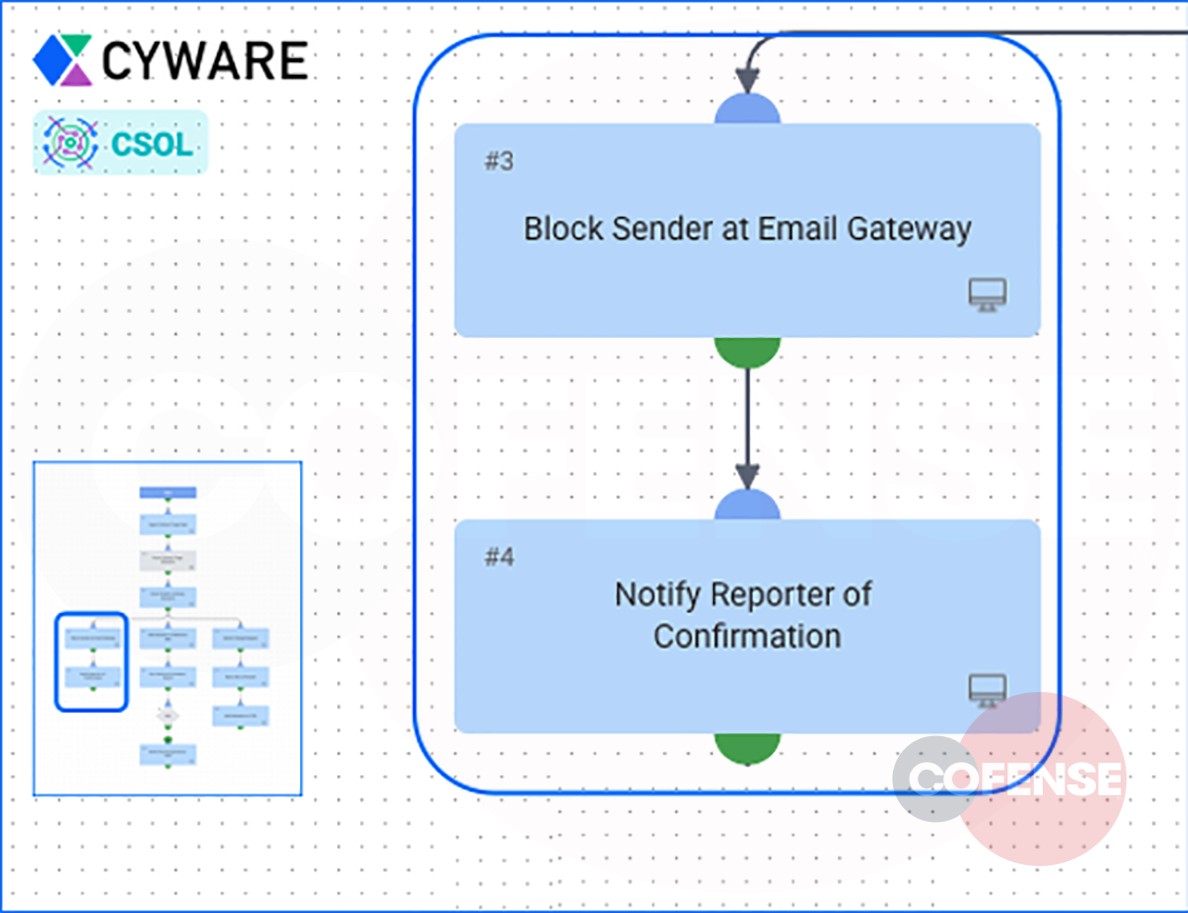
Figure 7. CSOL runs through remediation to block sender at the email gateway
7. Once enriched, the CSOL Playbook automated the mitigative action. The sender of the malicious email was automatically blocked at the email gateway and a confirmation notification was sent to the analyst.
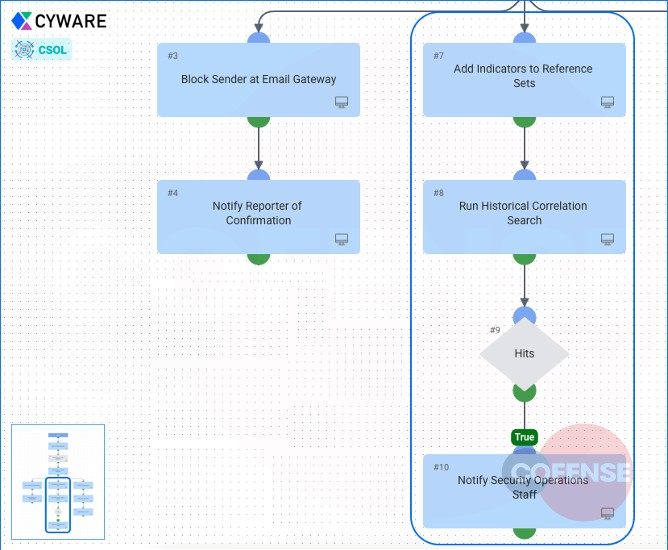
Figure 8. CSOL runs through additional steps from data received from Cofense
8. In addition, the malicious IOCs were sent to the SIEM to perform a historical lookup. If any of the malicious IOCs were previously seen in the organization’s environment, an alert was created and sent to the SOC team.
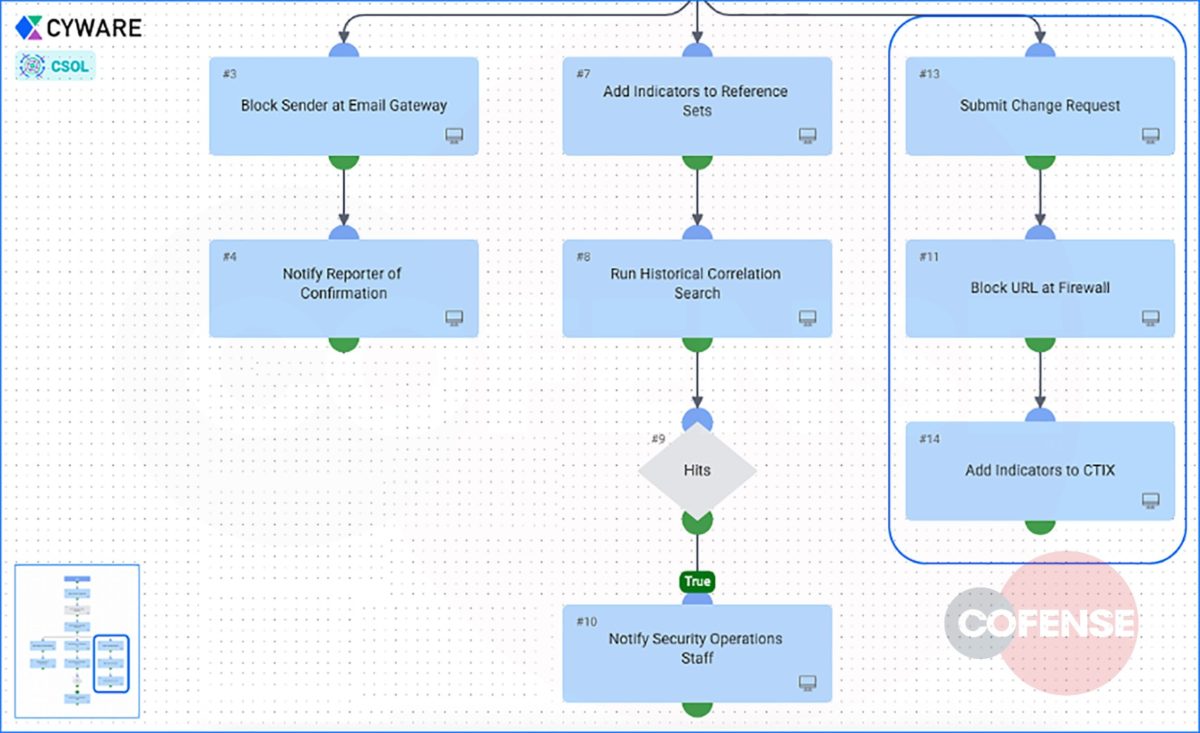
Figure 9. CSOL blocks URL at the firewall and ingests other indicators into CTIX
9. Finally, proactive defensive action was taken. The malicious URL was automatically blocked at the firewall, and all associated indicators were added to CTIX, Cyware’s Threat Intelligence Platform. Adding these indicators to CTIX ensures that this intelligence is memorialized and can be used at a later time for analytics, enrichment, and further correlation by the threat intel team.
The Cofense® and PhishMe® names and logos, as well as any other Cofense product or service names or logos displayed on this blog are registered trademarks or trademarks of Cofense Inc.
All third-party trademarks referenced by Cofense whether in logo form, name form or product form, or otherwise, remain the property of their respective holders, and use of these trademarks in no way indicates any relationship between Cofense and the holders of the trademarks. Any observations contained in this blog regarding circumvention of end point protections are based on observations at a point in time based on a specific set of system configurations. Subsequent updates or different configurations may be effective at stopping these or similar threats.
This post was first first published on Cofense’s website by Mike Saurbaugh. You can view it by clicking here